Using Mind Mapping to Develop a WBS
- shruti rabara
- Sep 25, 2021
- 5 min read
Updated: Dec 5, 2021
In project scope management is a critical part of project management that involves defining and controlling the work that will or will not be part of the project. After that work is defined, in terms of collecting the requirements and defining the scope, the next step is to divide and organize it into logical parts based on how it will be performed. This can easily be done using a work breakdown structure (WBS). Since a lot of major projects involve many people and various deliverables, a WBS acts as a deliverable-oriented grouping of work within a project that helps define its total scope. More so, it acts as a foundation document, providing a basis for managing and planning various aspects of the projects such as schedules, costs, resources and changes. Since a WBS helps to organize and define the total scope of a project, it can be seen as crucial to create a comprehensive and complete WBS.
A WBS often looks like a task-oriented tree made up of activities, to help visualize the project as a whole and all of its main parts. Here is an example of a WBS of the construction of a house.

The first level represents the entire project, construction of a house. The second level shows the main products to be delivered, which in this example, includes internal, foundation and external parts of building a house. The next levels describe the items within the main components.
While WBS can come in other forms, they can also be developed in a variety of methods as well. One of these methods include mind mapping. This is a technique that involves branches stemming from a core idea, in order to structure ideas and thoughts. This approach is distinguable in that it allows for more creativity because it is a more visual method to write or draw pictures of ideas in a format that is nonlinear.
Another key attribute of utilizing the mind mapping approach for creating a WBS is the ability to use software while doing this approach. Furthermore, there are a variety of softwares that allows you to use mind mapping to create a WBS, such as MatchWare’s MindView, Microsoft Visio and even Lucidchart.
Mind maps can be the most effective way to make a WBS once a team has considered the pros and cons of different possible courses of actions and selected one that better meets their constraints and overall goals. Once these things have been taken care of, the selected idea can be further explored.
An example given in pmi.org includes looking at a community fundraising team that has selected a 10K fun run to do. When creating this map, the team members should ask themselves, what are all the things that need to be done to complete the run. Considering the different parameters of the major deliverables, the members can start to brainstorm ideas for the map. The following is a high-level WBS mind map of the 10K fun run.

If a WBS includes various different types of deliverables, mind mapping can be done in multiple stages. For instance, the team can create a map of all the deliverables and only identify the high level tasks for the deliverables. Then, they can work together or in sub groups to create a sub-project mind map. The following is a more detailed mind map for the promotion portion of the 10K fun run.
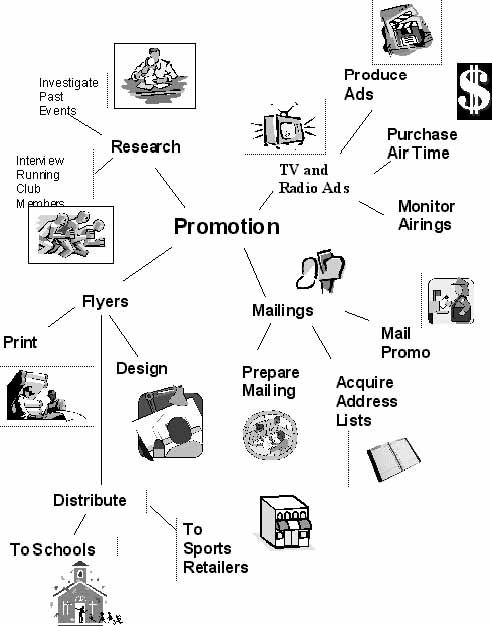
Once all the necessary WBS details are developed in one or more mind maps, a key step should be to analyze, consolidate and organize the ideas contained within. More so, a refined mind map can be produced as a result of analysis and can be reviewed and approved by the rest of the team.
Some of the benefits of using mind mapping to develop a WBS is that it helps to bring out more ideas than an outlining exercise that consists of using a more linear approach. One of the more interesting reasons this process helps bring forth more creativity is that it mimics human thought processing. The use of images, color, and line connections helps bring out our thoughts on paper more easily because of the complex ways of thinking we have. This approach also has been to be more engaging for team members, making it a more effective use. Another observation from teams that use mind mapping is the increase in contribution and speed. It is easier for team members to contribute ideas on a more spacious chart and how quickly ideas can be generated in it.
Although mind mapping has many advantages to using it, there are ways to ensure this approach works in the most efficient way possible. Some tips suggested by pmi.org include using a large piece of paper and posting it horizontally on a wall. By orienting it in landscape mode, it helps the right side of the brain, which is linked to creativity. Additionally, by setting the paper on a wall, team members can participate equally, than if it were on a table facing only one direction. This website also encourages the use of colors and having multiple members carry a pen to contribute to the map. Team members should not be worried about being messy and should create a smaller draft before placing the map on a larger piece of paper. Moreover, encourage members to draw images to help bring out more ideas and use keywords instead of sentences.
Once the WBS is completed after using the mind mapping approach, the project team should be ready for the next stage in the project planning process. After creating a big picture of the project through this mind mapping approach and taking into considerations the possible risks and build-in plans for avoiding them, responding to them or mitigating the consequence, members can go on to ask, “Given the scope and content of our plan, what are all the possibilities of mistakes that can happen in this project? After considering this question, the group can decide to make changes to the mind map, possibly adding or deleting portions of the WBS based on the overall analysis. In conclusion, it is crucial that in this early stage of project planning, there is a lot of team involvement and creativity. Using a mind map clearly meets both of these attributes and helps to create the more effective WBS, as possible.
Bibliography
MatchWare. “Construction of a House - WBS.” matchware.com, https://www.matchware.com/examples/mind-map/construction-of-a-house/553.
Schwalbe, Kathy. InformatIon technology Project ManageMent. 9th ed., Professor Emeritus, Augsburg College, 2018.
Brown, K. A. & Hyer, N. L. (2001). Mind mapping as a WBS development tool. Paper presented at Project Management Institute Annual Seminars & Symposium, Nashville, TN. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute.


Comments